low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism
When this happens in late-stage COPD when a person has severely weakened respiratory muscles the condition may lead to respiratory failure. This volume is considered to be 30 of.
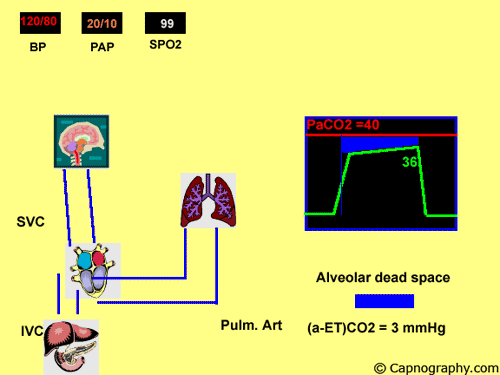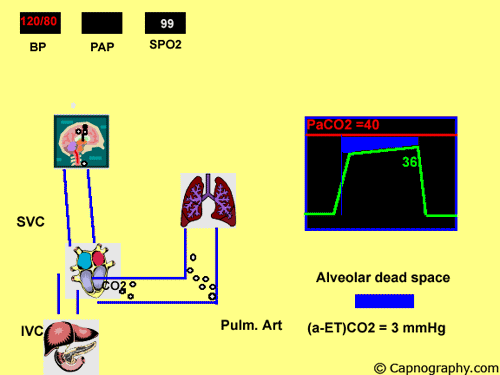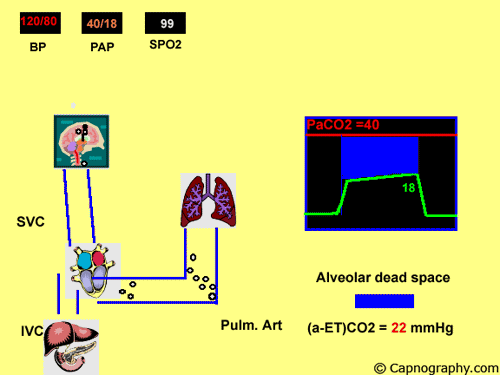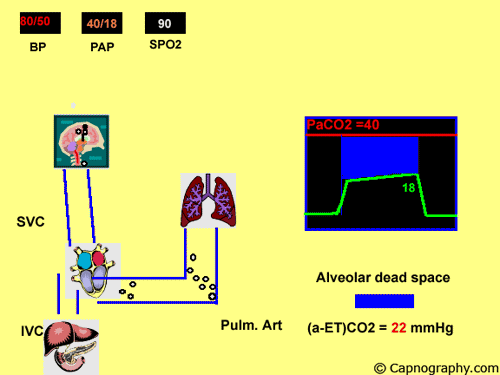
Detection Of Pulmonary Air Embolism Capnography
More than 20 000 infants and children have a cardiac arrest per year in the United States.

. In people with COPD who have serious breathing problems the increased CO2 level can result in what is called respiratory acidosis. Follow end tidal CO2. What is the best action.
Target the usual oxygen CO2 levels as for any critically ill patient. Acute pulmonary embolism D hyperventilation syndrome. The Journal of Pediatrics is an international peer-reviewed journal that advances pediatric research and serves as a practical guide for pediatricians who manage health and diagnose and treat disorders in infants children and adolescentsThe Journal publishes original work based on standards of excellence and expert review.
A ineffective chest compressions. Use capnography to verify exhaled CO2 Observe chest wall movement. Measuring exhaled carbon dioxide End Tidal CO2 ETCO2 is an important ICU technology that can used to confirm ETT placement to ensure safer procedural sedation to guide ACLSresuscitation and to monitor cardiac and pulmonary physiology in realtimeThis ICU.
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO 2 in the respiratory gasesIts main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive careIt is usually presented as a graph of CO 2 measured in millimeters of mercury mmHg plotted against time or less commonly but more usefully expired. 106 This and subsequent studies recommend ventilating patients to maintain V t of 6 to 8 mLkg predicted body weight and inspiratory plateau pressure 30 cm H 2 O to reduce. Combining D-dimer results with measurement of the exhaled end-tidal ratio of.
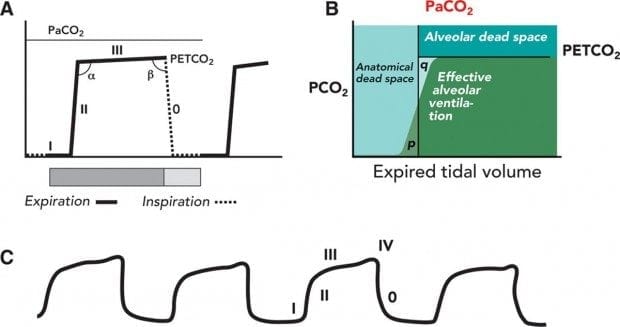
The two types of dead space are anatomical dead space and physiologic dead space. Hypocapnia from the Greek words υπό meaning below normal and καπνός kapnós meaning smoke also known as hypocarbia sometimes incorrectly called acapnia is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the bloodHypocapnia usually results from deep or rapid breathing known as hyperventilation. The nurse assesses the client and then attempts to determine the cause of the alarm.
Use an end-tidal CO2 monitor to check for placement in the trachea. This may improve oxygen carrying capacity thereby improving oxygen delivery to the tissues. CriticalCare ICUEquipment ventilation waveforms monitors.
A sudden increase in end-tidal CO2 may be the earliest indicator of. Pulmonary embolism Myasthenia gravis COPD Orthopnea. This monthly journal offers comprehensive coverage of new techniques important developments and innovative ideas in oral and maxillofacial surgeryPractice-applicable articles help develop the methods used to handle dentoalveolar surgery facial injuries and deformities TMJ disorders oral cancer jaw reconstruction anesthesia and analgesiaThe journal also.
The Journal seeks to publish high. Starting the patient on a low tidal volume. What diagnostic study is preferred.
14 In 2015 emergency medical servicedocumented out-of-hospital cardiac arrest OHCA occurred in more than 7000 infants and children. Characteristic signs of epiglottitis include a low-grade fever a seal-like barking cough and varying degrees of respiratory distress. For patients with pulmonary embolism thrombolysis may be considered in the context of life-threatening and refractory hypoxemia.
In Fowlers position the patient is at an increased risk for air embolism skin injury from shearing and sliding and DVT forming in the patients lower extremities. Negative results on a high-sensitivity D-dimer test in a patient with a low pretest probability of pulmonary embolism indicate a low likelihood of venous thromboembolism and reliably exclude pulmonary embolism. Displaced endotracheal tube.
Acute cor pulmonale due to massive pulmonary embolism. Upper airway obstruction eg choking angioedema. 4 Approximately 114 of pediatric OHCA patients survived to hospital discharge but outcomes varied by age with survival rates of 171 in adolescents.
When CO2 is elevated it creates an acidic environment. The patients arms should be flexed and secured across the body the buttocks should be padded and the knees flexed 30 degrees. The low-pressure alarm sounds on a ventilator.
B inadvertent ET tube dislodgment. If unsuccessful in determining the cause of the alarm the nurse should take. Can the value of end tidal CO2 prognosticate ROSC in patients coding into emergency department with an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
If the water bath temperature is very low this is a contraindication to removing cooling pads. The biggest drawback of PSV is its unreliable tidal volumes that may generate CO2 retention and acidosis as well as the higher work of breathing which can lead to respiratory fatigue. It is important to keep the airway pressures low to avoid increased intracranial pressures.
Hypocapnia is the opposite of hypercapnia. Consider administration of furosemide along with blood to avoid volume overload. 20 bpm ACPC ventilation.
Dead space represents the volume of ventilated air that does not participate in gas exchange. Low tidal volume ventilation has been shown to be lung protective not only in ARDS but in other types of diseases. D-dimer and exhaled CO2O2 to detect.
Anatomical dead space is represented by the volume of air that fills the conducting zone of respiration made up by the nose trachea and bronchi. Increase the low tidal volume alarm to 600 mL Decrease the high pressure limit to 45-50 cmH2O. Savastano S et al.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and defibrillation success in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. In a comparison of high- and low-tidal-volume ventilation the death rate of patients with ARDS was reduced from 40 to 31 in the group with reduced tidal volume V t. You have a patient with a pulmonary embolism.

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

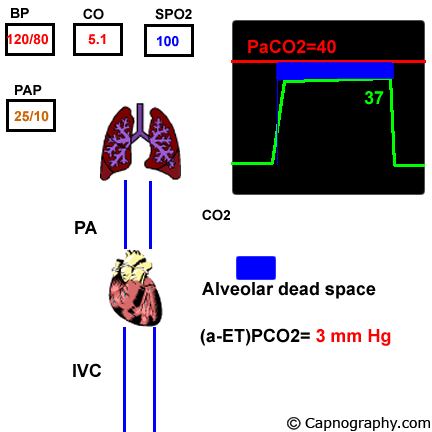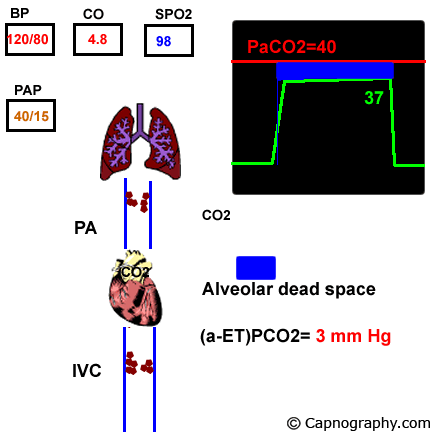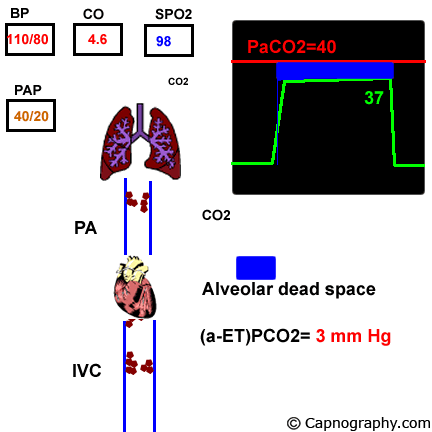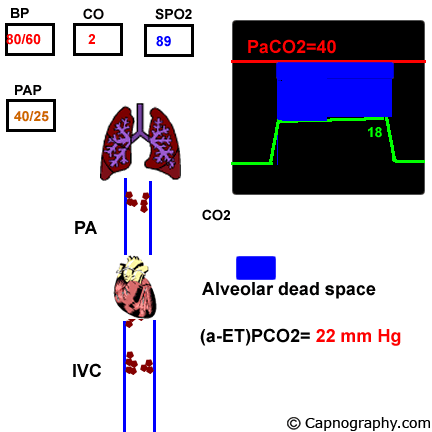
Capnography And Pulmonary Embolism Chapter 21 Capnography

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Basics Of Waveform Capnography Waveform Capnography Grepmed

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News